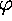 (t) with x = r cos(
(t) with x = r cos(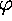 ), y = r sin(
), y = r sin(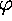 ).
).Instead of x(t), y(t) we will use polar
coordinates r(t), 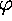 (t) with x = r cos(
(t) with x = r cos(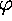 ), y = r sin(
), y = r sin(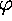 ).
).
An example of a proper node for a linear system is given
by
x' = -xor, in polar coordinates,
y' = -y
r' = -r
' = 0
r' = -rIn this case all trajectories except one approach the critical point from one direction (
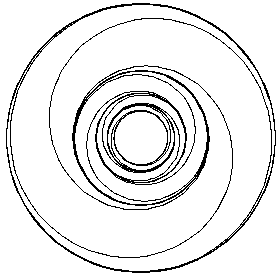
' = sin(
) / log(r)
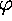 = 0),
not all directions as for a proper node, or two directions
as for a node or improper node.
= 0),
not all directions as for a proper node, or two directions
as for a node or improper node. An example of a center for a linear system is given by
x' = -yor, in polar coordinates,
y' = x
r' = 0
' = 1
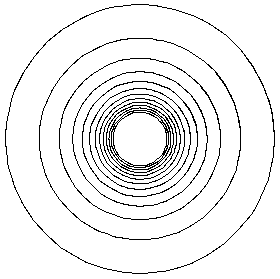
r' = r^2 sin(1/r)In this case there are infinitely many limit cycles at r = 1/
' = 1
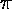 , 1/(2
, 1/(2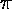 ), 1/(3
), 1/(3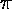 ), ... which are approached by the trajectories in between.
), ... which are approached by the trajectories in between.